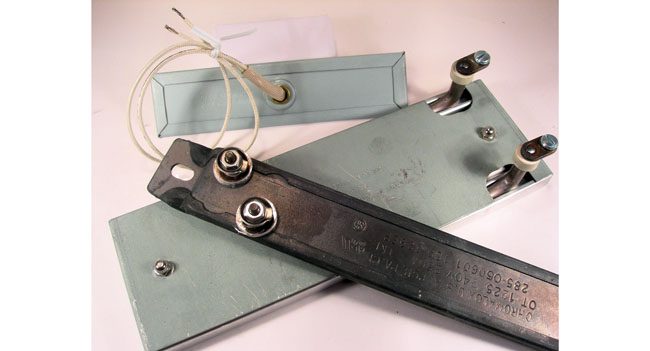
What Are Industrial Strip Heaters?
An industrial strip heater, sometimes called a component heater, is unique in that it can provide both convective heat (indirect heating by warm air) and radiant heat (direct heating through the surface of a material). In an industrial setting, the strip heater is bolted or clamped directly onto an object or placed within an environment to provide heat over a large area. They may also have fins that allow them to maximize heated surface area and increase heat transfer.
How Strip Heaters Are Constructed

Strip heaters are designed with a metal heating element that’s contained within a protective sheath and insulated with mica, magnesium oxide, or ceramic materials. The actual jacket is constructed of aluminum, iron, steel, stainless steel, or other alloy for ease of heat transfer.
Common Uses
Strip heaters are great for most surface heating and process air heating applications, including:
Advantages
- Easy Installation: Strip heaters are easy to modify and mount to your equipment.
- High Operating Temperatures: While the resistance varies by design, mica, channel, and mineral-insulated heaters have high operating temperatures.
- Fully Customizable: Strip heaters can be designed for your specific applications. Customizable features include strip length, width and thickness, termination types, and power and electrical output requirements.
- Versatility: Strip heaters have incredibly versatile designs that make them suitable for many applications.
Types of Strip Heaters
Mica

Mica heaters feature a high-temperature oxidation metal sheath and high-grade mica insulation resistant to moisture and high temperatures up to 900 degrees Fahrenheit. Nickel/chromium resistance wire is evenly wound around the heating element, providing uniform and reliable heat distribution. They come in many shapes, sizes, and termination options, and can even be manufactured with holes in them.
Mineral Insulated

Mineral insulated heaters are thin, responsive heaters with a nickel-chromium element wire embedded in them. They can withstand temperatures reaching 1,400 degrees Fahrenheit.
Channel

Channel heaters feature a helically wound resistance coil that’s evenly strung through specially designed ceramic insulators. These durable heaters can get extremely hot (up to 1,100 degrees Fahrenheit). However, they come in one width and one shape, and are not as customizable.
Is a Strip Heater Right for Your Application?
Your specific application will determine the type of heater you need. Strip heaters are best for direct conduction heating, flat surface heating, medium-temperature applications, and space-constrained installations.
Some of the many factors you will need to consider when selecting a strip heater include:
- Physical Dimensions: Required length, width, or thickness.
- Power Requirements: Watt density, maximum operating temperature, and AC voltage determined by the application.
- Required Features: Coil patterns, enclosed sides, corrosion resistance, open elements, instrumentation cutouts, etc.
- Termination Types: Tandem posts, parallel posts, insulated leads, flexible conduit leads, etc.
Installation Tips
Correct installation and operation of an industrial strip heater is critical to obtaining an extended service life and the best operational performance. Exposing the heater and/or terminals to voltages or temperatures above the manufacturer’s recommendations can cause premature failure.
Additionally, environmental contaminants like oil, dirt, plastics, and even moisture that may travel to the heater windings can cause a short circuit or heater failure.
Here are some tips on how to correctly install your strip heater:
- Surface-mounted mica strip heaters should be clamped securely along their entire length to a smooth metal surface, using the mounting slots and metal clamps placed 76 to 127 millimeters (3 to 5 inches) apart.
- The terminal end should be secured firmly, even when supported at the mounting slots, ensuring one end is slightly loosened to allow for linear expansion.
- The surface being heated should be as clean and smooth as possible for the most efficient heat transfer and to eliminate small air gaps that can cause hot spots.
- Do not over-tighten terminal posts because excessive torque could break the wired connection.
Find Your Solution
Hi-Watt has been Michigan’s leading distributor of industrial heating solutions for over 40 years. We supply and configure strip heaters from top brands such as Watlow, Tempco, and Chromalox.
Our expert team can help you select and configure the best heating solution for your facility, along with integration/installation assistance and ongoing field services.
Contact us today to talk to an application specialist.
